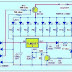
This simplest electronic choke can be built low cost, it can glow open tubelights too, no need of a new .
Working voltage: 170~300V for 220V tube, 80~140V for 110V tube.
PARTS LIST:
Diode: IN4007(MIC) x4
Capacitor: 2.2/800(KELTRON) x2
Neon lamp(optional)x1
Not mentioning 100Watt bulb or other inductor, as we can get it in our house.
Working voltage: 170~300V for 220V tube, 80~140V for 110V tube.
You can use a tungsten bulb of 100Watt rating of 230V/110V as the series inductor, U can use Existing Choke, or use fan regulator coil, or even Soldering Iron coil(min65W). For the diodes, IN4007 has reverse voltage protection of 1000V, use this of good company(i.e, MIC, ST,BEL). Using low cost diodes can blow the capacitors. For capacitors, use Keltron or any other good company. You can use 400V capacitor if you cannot find 800V one.
PARTS LIST:
Diode: IN4007(MIC) x4
Capacitor: 2.2/800(KELTRON) x2
Neon lamp(optional)x1
Not mentioning 100Watt bulb or other inductor, as we can get it in our house.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed Twitter
Twitter 9:45 AM
9:45 AM
 ADMIN
ADMIN